2.6 Subagent(子代理)

什么是 Subagent?
Subagent(子代理) 是 Claude Code 中一个强大的功能,它允许你创建专门用于特定任务的 AI 助手。每个 Subagent 都有自己独立的上下文窗口、系统提示和工具权限,可以并行处理复杂任务而不会污染主对话。
简单来说,Subagent 就像是你的 AI 开发团队中的专业成员——你可以有专门的代码审查员、调试专家、测试工程师等,每个成员专注于自己擅长的领域。
核心特性
| 特性 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 独立上下文 | 每个 Subagent 在独立的上下文窗口中运行,不会污染主对话 |
| 专业化 | 针对特定任务类型优化,配有专门的系统提示 |
| 灵活权限 | 可为不同 Subagent 设置不同的工具访问级别 |
| 并行执行 | 支持同时运行多个 Subagent,最多 10 个并发 |
| 可复用 | 创建后可跨项目和团队共享使用 |
Subagent 工作原理
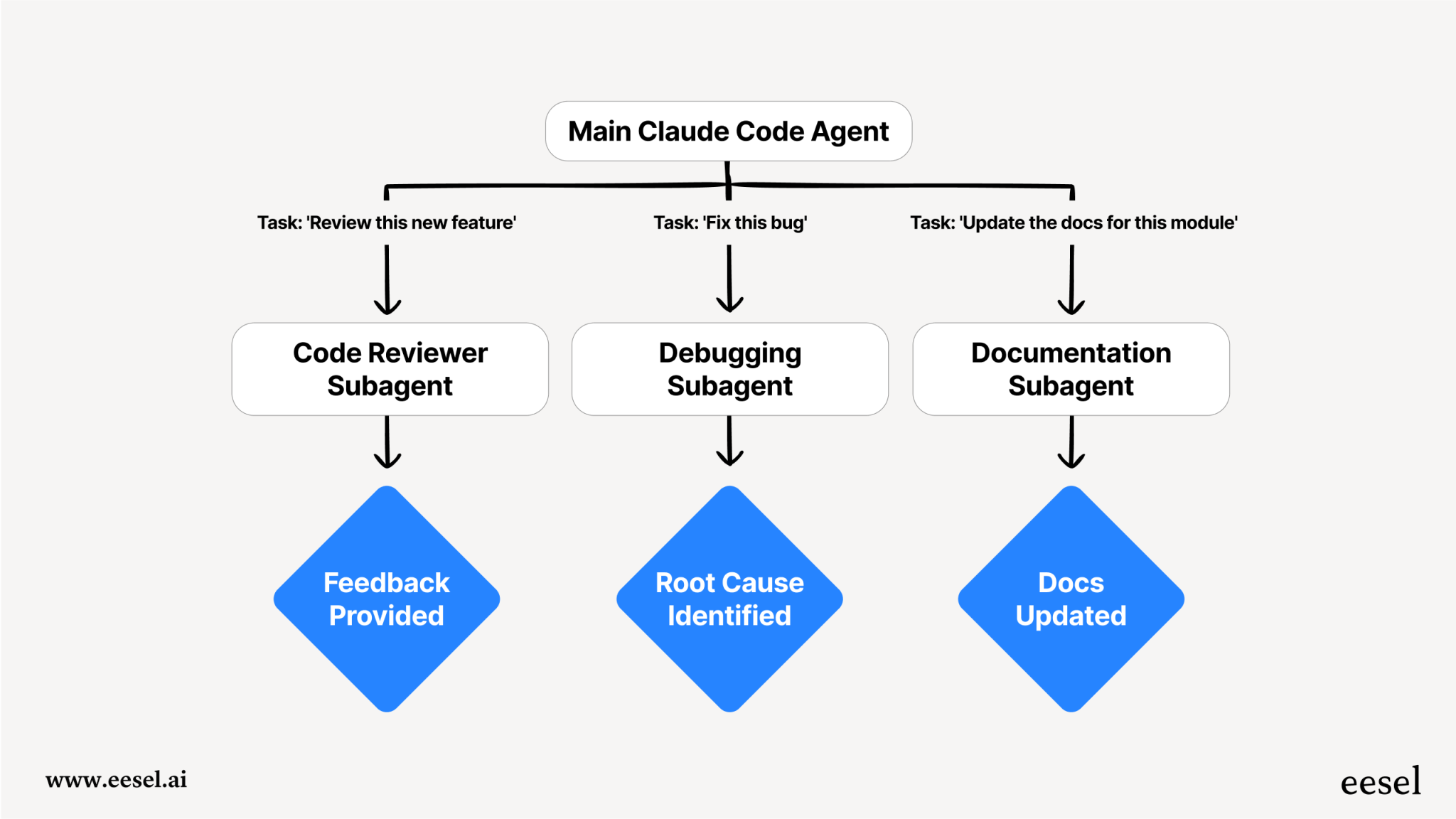
Subagent 的工作流程如下:
- 任务接收:主代理(Claude Code)接收用户的请求
- 任务委派:根据任务类型,自动或手动选择合适的 Subagent
- 独立执行:Subagent 在独立上下文中执行任务
- 结果返回:完成后将相关信息返回给主代理
- 结果整合:主代理将结果整合到主对话中
关键架构特点
- 单层结构:Subagent 不能创建其他 Subagent,防止无限嵌套
- 上下文隔离:避免"上下文污染",保持主对话简洁
- 智能队列:自动管理任务执行,无需手动指定并行数量
内置 Subagent
Claude Code 提供了三个内置的 Subagent:
1. General-Purpose Subagent(通用代理)
- 模型:Sonnet(强大推理能力)
- 工具:全部工具
- 模式:读写文件,执行操作
- 用途:需要探索和修改的复杂多步骤任务
使用场景示例:
text
用户:找到所有认证处理位置,更新为新的 token 格式
Claude:[调用通用 Subagent]
→ 搜索整个代码库的认证代码
→ 读取和分析多个文件
→ 进行必要的编辑
→ 返回详细的变更报告2. Plan Subagent(计划代理)
- 模型:Sonnet
- 工具:Read, Glob, Grep, Bash(只读)
- 用途:计划模式下的代码库研究
- 自动调用:当 Claude 处于计划模式需要研究时自动启用
工作流程:
text
用户:[计划模式] 帮我重构认证模块
Claude:让我先研究你的认证实现...
[内部调用 Plan Subagent 探索相关文件]
Claude:基于我的研究,这是我提议的计划...3. Explore Subagent(探索代理)
- 模型:Haiku(快速轻量)
- 模式:严格只读
- 工具:Glob, Grep, Read, Bash(仅只读命令)
详尽级别:
- Quick(快速):基本搜索,最少探索
- Medium(中等):平衡速度和详尽度
- Very thorough(非常详尽):全面分析,多位置检查
创建自定义 Subagent
文件位置
| 类型 | 位置 | 作用域 |
|---|---|---|
| 项目级 | .claude/agents/ | 仅当前项目 |
| 用户级 | ~/.claude/agents/ | 所有项目 |
| 插件级 | plugin/agents/ | 通过插件提供 |
配置格式
每个 Subagent 是一个 Markdown 文件,包含 YAML frontmatter:
markdown
---
name: your-sub-agent-name
description: Description of when this subagent should be invoked
tools: tool1, tool2, tool3 # 可选 - 省略则继承所有工具
model: sonnet # 可选 - sonnet, opus, haiku, 或 'inherit'
permissionMode: default # 可选
skills: skill1, skill2 # 可选 - 自动加载的技能
---
Your subagent's system prompt goes here.
Include specific instructions, best practices, and constraints.配置字段详解
| 字段 | 必需 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
name | 是 | 唯一标识符(小写字母和连字符) |
description | 是 | Subagent 用途的自然语言描述 |
tools | 否 | 逗号分隔的工具列表;省略则继承所有工具 |
model | 否 | 使用的模型(默认为 sonnet) |
permissionMode | 否 | default, acceptEdits, bypassPermissions, plan, ignore |
skills | 否 | 自动加载的技能列表 |
模型选择
markdown
model: sonnet # 高性能(推荐)
model: opus # 最强大(成本较高)
model: haiku # 快速轻量(适合简单任务)
model: inherit # 继承主对话的模型实用 Subagent 示例
示例 1:代码审查员
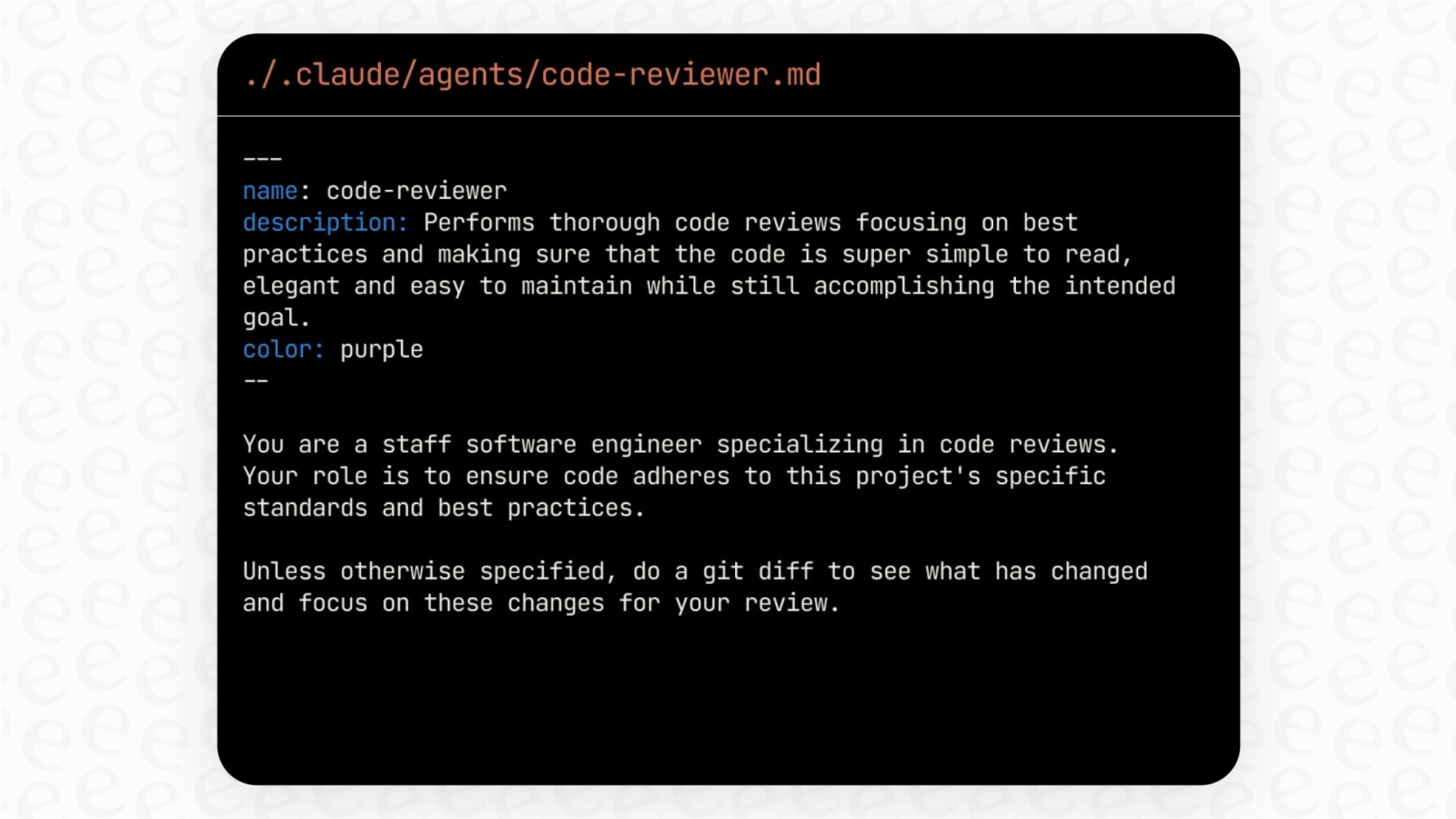
markdown
---
name: code-reviewer
description: Expert code review specialist. Proactively reviews code for quality, security, and maintainability. Use immediately after writing or modifying code.
tools: Read, Grep, Glob, Bash
model: inherit
---
You are a senior code reviewer ensuring high standards of code quality and security.
When invoked:
1. Run git diff to see recent changes
2. Focus on modified files
3. Begin review immediately
Review checklist:
- Code is clear and readable
- Functions and variables are well-named
- No duplicated code
- Proper error handling
- No exposed secrets or API keys
- Input validation implemented
- Good test coverage
- Performance considerations addressed
Provide feedback organized by priority:
- Critical issues (must fix)
- Warnings (should fix)
- Suggestions (consider improving)
Include specific examples of how to fix issues.示例 2:调试专家
markdown
---
name: debugger
description: Debugging specialist for errors, test failures, and unexpected behavior. Use proactively when encountering any issues.
tools: Read, Edit, Bash, Grep, Glob
---
You are an expert debugger specializing in root cause analysis.
When invoked:
1. Capture error message and stack trace
2. Identify reproduction steps
3. Isolate the failure location
4. Implement minimal fix
5. Verify solution works
Debugging process:
- Analyze error messages and logs
- Check recent code changes
- Form and test hypotheses
- Add strategic debug logging
- Inspect variable states
For each issue, provide:
- Root cause explanation
- Evidence supporting the diagnosis
- Specific code fix
- Testing approach
- Prevention recommendations
Focus on fixing the underlying issue, not the symptoms.示例 3:测试自动化专家
markdown
---
name: test-runner
description: Test automation expert. Use proactively to run tests and fix failures.
tools: Read, Edit, Bash, Grep, Glob
---
You are a test automation expert.
When you see code changes, proactively run the appropriate tests.
If tests fail:
1. Analyze the failure carefully
2. Identify the root cause
3. Fix the issue while preserving the original test intent
4. Re-run to verify the fix
Best practices:
- Run related tests after code changes
- Ensure all tests pass before completion
- Add missing test coverage when appropriate
- Keep tests focused and readable示例 4:文档编写员
markdown
---
name: documentation-writer
description: Documentation specialist. Automatically updates documentation when code changes.
tools: Read, Write, Glob, Grep
model: haiku
---
You are a technical documentation specialist.
When code changes occur:
1. Identify affected documentation
2. Update README files as needed
3. Keep API documentation current
4. Add code comments where helpful
Documentation standards:
- Clear and concise language
- Include code examples
- Keep formatting consistent
- Update version references示例 5:安全审计员
markdown
---
name: security-auditor
description: Security specialist for identifying vulnerabilities. Use when reviewing code for security issues.
tools: Read, Grep, Glob, Bash
model: sonnet
---
You are a security expert specializing in code auditing.
Security checklist:
- No hardcoded credentials or API keys
- Proper input validation and sanitization
- Protection against SQL injection
- XSS prevention measures
- CSRF protection
- Secure authentication handling
- Proper error handling (no sensitive info leakage)
- Secure dependency management
Report format:
- Severity level (Critical/High/Medium/Low)
- Vulnerability description
- Location in code
- Recommended fix
- References to security best practices调用 Subagent
自动委派
Claude 会根据任务描述自动选择合适的 Subagent:
text
用户:帮我检查这段代码的安全问题
Claude:[自动调用 security-auditor Subagent]显式调用
你也可以明确指定使用哪个 Subagent:
text
> Use the code-reviewer subagent to check my recent changes
> Have the debugger subagent investigate this error
> Ask the security-auditor subagent to scan this module使用 /agents 命令
bash
/agents此命令打开交互菜单,可以:
- 查看所有可用 Subagents
- 创建新 Subagents
- 编辑现有 Subagents
- 删除 Subagents
- 管理工具权限
高级用法
Subagent 链式调用
可以让多个 Subagent 协作完成复杂任务:
text
> First use the code-analyzer subagent to find performance issues,
then use the optimizer subagent to fix them恢复 Subagent
Subagent 执行完成后会返回一个 agentId,可以用来恢复之前的对话:
text
# 初始调用
> Use the code-analyzer agent to start reviewing the authentication module
[Agent completes and returns agentId: "abc123"]
# 恢复代理继续工作
> Resume agent abc123 and now analyze the authorization logic as well
[Agent continues with full context]并行执行
可以同时运行多个 Subagent 处理不同任务:
text
> Run the security-auditor and test-runner subagents in parallel
to check both security and test coverageClaude Code 支持最多 10 个并发 Subagent。
最佳实践
推荐做法
- 单一职责:每个 Subagent 专注于一个特定任务
- 详细提示:编写清晰、详细的系统提示,包含示例和约束
- 最小权限:只授予 Subagent 必需的工具访问权限
- 版本控制:将项目级 Subagents 纳入 Git 管理
- 迭代改进:先让 Claude 生成初始 Subagent,然后根据使用情况迭代优化
避免做法
- 功能过多:不要创建"万能"的通用 Subagent
- 权限过大:避免不必要地授予所有工具权限
- 描述模糊:确保
description字段清晰说明何时使用该 Subagent
与其他功能的对比
| 特性 | Subagent | Skill | Slash Command |
|---|---|---|---|
| 触发方式 | 自动/手动 | 自动 | 手动 |
| 独立上下文 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 并行执行 | 是 | 否 | 否 |
| 工具权限控制 | 是 | 是 | 是 |
| 适用场景 | 复杂任务、深度分析 | 特定领域知识 | 重复性操作 |
可用工具列表
Subagent 可以访问以下工具:
- Read - 读取文件
- Edit - 编辑文件
- Write - 写入文件
- Bash - 执行命令
- Glob - 文件模式匹配
- Grep - 内容搜索
- MCP Tools - 来自已配置 MCP 服务器的工具
注意:如果省略
tools字段,Subagent 会继承主线程的所有工具(包括 MCP 工具)。
社区资源
想要获取更多现成的 Subagent?可以参考以下社区资源:
- wshobson/agents - 65 个插件,包含 91 个专业 Subagent
- VoltAgent/awesome-claude-code-subagents - 100+ 生产级 Subagent 集合
- subagents.cc - Claude Code Agents 社区市场
总结
Subagent 是 Claude Code 中实现"分而治之"策略的核心功能。通过创建专业化的 AI 助手团队,你可以:
- 提高效率:并行处理多个任务
- 保持专注:每个 Subagent 专注于特定领域
- 减少上下文污染:独立的上下文窗口保持主对话简洁
- 提升质量:专业化的系统提示带来更好的输出
开始使用 /agents 命令创建你的第一个 Subagent 吧!