Adaptive RAG
基于 LangGraph 官方教程:结合查询分析与自纠正 RAG 的智能检索策略
概述
Adaptive RAG 是一种将 (1) 查询分析 (Query Analysis) 与 (2) 主动/自纠正 RAG (Active / Self-corrective RAG) 相结合的 RAG 策略。
根据 论文 的描述,查询分析可以路由到以下三种模式:
- No Retrieval:无需检索,直接使用 LLM 知识
- Single-shot RAG:单次 RAG 检索
- Iterative RAG:迭代式 RAG 检索
本教程使用 LangGraph 构建了一个改进版本,路由策略包括:
- Web Search:针对时效性问题(如近期事件)
- Self-corrective RAG:针对索引相关的问题
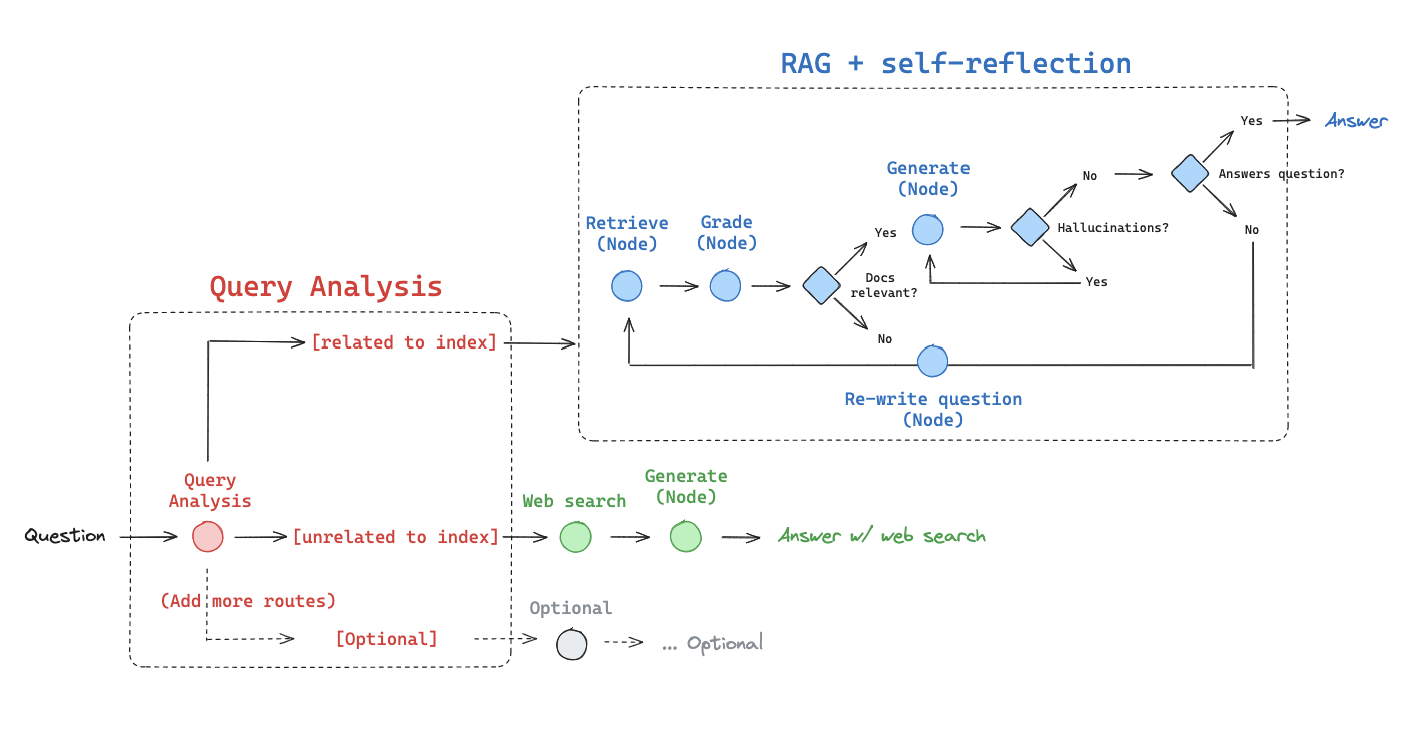 图:Adaptive RAG 系统架构
图:Adaptive RAG 系统架构
环境准备
安装依赖
bash
pip install -U langchain_community tiktoken langchain-openai langchain-cohere \
langchainhub chromadb langchain langgraph tavily-python设置 API Keys
python
import getpass
import os
def _set_env(var: str):
if not os.environ.get(var):
os.environ[var] = getpass.getpass(f"{var}: ")
_set_env("OPENAI_API_KEY")
_set_env("TAVILY_API_KEY")一、创建向量索引
使用 OpenAI Embeddings 和 Chroma 向量数据库,对博客文章进行索引:
python
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
# 设置 Embeddings
embd = OpenAIEmbeddings()
# 待索引的文档 URL
urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
# 加载文档
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
# 分割文档
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=500, chunk_overlap=0
)
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
# 添加到向量存储
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits,
collection_name="rag-chroma",
embedding=embd,
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()二、LLM 组件
2.1 查询路由器 (Router)
创建 RouteQuery 数据模型,让 LLM 决定将查询路由到向量存储还是 Web 搜索:
python
from typing import Literal
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# 数据模型
class RouteQuery(BaseModel):
"""Route a user query to the most relevant datasource."""
datasource: Literal["vectorstore", "web_search"] = Field(
...,
description="Given a user question choose to route it to web search or a vectorstore.",
)
# 带结构化输出的 LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm_router = llm.with_structured_output(RouteQuery)
# 提示词
system = """You are an expert at routing a user question to a vectorstore or web search.
The vectorstore contains documents related to agents, prompt engineering, and adversarial attacks.
Use the vectorstore for questions on these topics. Otherwise, use web-search."""
route_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system),
("human", "{question}"),
])
question_router = route_prompt | structured_llm_router
# 测试
print(question_router.invoke(
{"question": "Who will the Bears draft first in the NFL draft?"}
)) # -> web_search
print(question_router.invoke(
{"question": "What are the types of agent memory?"}
)) # -> vectorstore2.2 检索评分器 (Retrieval Grader)
评估检索到的文档是否与查询相关:
python
class GradeDocuments(BaseModel):
"""Binary score for relevance check on retrieved documents."""
binary_score: str = Field(
description="Documents are relevant to the question, 'yes' or 'no'"
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm_grader = llm.with_structured_output(GradeDocuments)
system = """You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question.
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the user question, grade it as relevant.
It does not need to be a stringent test. The goal is to filter out erroneous retrievals.
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question."""
grade_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system),
("human", "Retrieved document: \n\n {document} \n\n User question: {question}"),
])
retrieval_grader = grade_prompt | structured_llm_grader2.3 生成器 (Generator)
使用 RAG 提示词生成答案:
python
from langchain import hub
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# 从 Hub 拉取 RAG 提示词
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
# RAG Chain
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()2.4 幻觉评分器 (Hallucination Grader)
验证生成的答案是否基于检索到的事实:
python
class GradeHallucinations(BaseModel):
"""Binary score for hallucination present in generation answer."""
binary_score: str = Field(
description="Answer is grounded in the facts, 'yes' or 'no'"
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm_grader = llm.with_structured_output(GradeHallucinations)
system = """You are a grader assessing whether an LLM generation is grounded in / supported by a set of retrieved facts.
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no'. 'Yes' means that the answer is grounded in / supported by the set of facts."""
hallucination_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system),
("human", "Set of facts: \n\n {documents} \n\n LLM generation: {generation}"),
])
hallucination_grader = hallucination_prompt | structured_llm_grader2.5 答案评分器 (Answer Grader)
评估答案是否真正回答了问题:
python
class GradeAnswer(BaseModel):
"""Binary score to assess answer addresses question."""
binary_score: str = Field(
description="Answer addresses the question, 'yes' or 'no'"
)
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm_grader = llm.with_structured_output(GradeAnswer)
system = """You are a grader assessing whether an answer addresses / resolves a question.
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no'. 'Yes' means that the answer resolves the question."""
answer_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system),
("human", "User question: \n\n {question} \n\n LLM generation: {generation}"),
])
answer_grader = answer_prompt | structured_llm_grader2.6 查询重写器 (Question Rewriter)
优化查询以提高检索效果:
python
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
system = """You a question re-writer that converts an input question to a better version that is optimized
for vectorstore retrieval. Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning."""
re_write_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages([
("system", system),
("human", "Here is the initial question: \n\n {question} \n Formulate an improved question."),
])
question_rewriter = re_write_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()三、Web 搜索工具
使用 Tavily Search 获取网络信息:
python
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
web_search_tool = TavilySearchResults(k=3)四、构建 LangGraph 工作流
4.1 定义状态
python
from typing import List
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""
Represents the state of our graph.
Attributes:
question: question
generation: LLM generation
documents: list of documents
"""
question: str
generation: str
documents: List[str]4.2 定义节点函数
python
from pprint import pprint
from langchain.schema import Document
def retrieve(state):
"""检索文档"""
print("---RETRIEVE---")
question = state["question"]
documents = retriever.invoke(question)
return {"documents": documents, "question": question}
def generate(state):
"""生成答案"""
print("---GENERATE---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
docs_txt = format_docs(documents)
generation = rag_chain.invoke({"context": docs_txt, "question": question})
return {"documents": documents, "question": question, "generation": generation}
def grade_documents(state):
"""评估文档相关性"""
print("---CHECK DOCUMENT RELEVANCE TO QUESTION---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
filtered_docs = []
for d in documents:
score = retrieval_grader.invoke(
{"question": question, "document": d.page_content}
)
grade = score.binary_score
if grade == "yes":
print("---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---")
filtered_docs.append(d)
else:
print("---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---")
continue
return {"documents": filtered_docs, "question": question}
def transform_query(state):
"""重写查询"""
print("---TRANSFORM QUERY---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
better_question = question_rewriter.invoke({"question": question})
return {"documents": documents, "question": better_question}
def web_search(state):
"""Web 搜索"""
print("---WEB SEARCH---")
question = state["question"]
docs = web_search_tool.invoke({"query": question})
web_results = "\n".join([d["content"] for d in docs])
web_results = Document(page_content=web_results)
return {"documents": web_results, "question": question}4.3 定义路由函数(边)
python
def route_question(state):
"""路由问题到 Web 搜索或 RAG"""
print("---ROUTE QUESTION---")
question = state["question"]
source = question_router.invoke({"question": question})
if source.datasource == "web_search":
print("---ROUTE QUESTION TO WEB SEARCH---")
return "web_search"
elif source.datasource == "vectorstore":
print("---ROUTE QUESTION TO RAG---")
return "vectorstore"
def decide_to_generate(state):
"""决定是生成答案还是重写查询"""
print("---ASSESS GRADED DOCUMENTS---")
filtered_documents = state["documents"]
if not filtered_documents:
print("---DECISION: ALL DOCUMENTS ARE NOT RELEVANT TO QUESTION, TRANSFORM QUERY---")
return "transform_query"
else:
print("---DECISION: GENERATE---")
return "generate"
def grade_generation_v_documents_and_question(state):
"""评估生成内容:是否有幻觉、是否回答了问题"""
print("---CHECK HALLUCINATIONS---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
generation = state["generation"]
score = hallucination_grader.invoke(
{"documents": documents, "generation": generation}
)
grade = score.binary_score
if grade == "yes":
print("---DECISION: GENERATION IS GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS---")
print("---GRADE GENERATION vs QUESTION---")
score = answer_grader.invoke({"question": question, "generation": generation})
grade = score.binary_score
if grade == "yes":
print("---DECISION: GENERATION ADDRESSES QUESTION---")
return "useful"
else:
print("---DECISION: GENERATION DOES NOT ADDRESS QUESTION---")
return "not useful"
else:
pprint("---DECISION: GENERATION IS NOT GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS, RE-TRY---")
return "not supported"4.4 编译图
python
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph, START
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# 添加节点
workflow.add_node("web_search", web_search)
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieve)
workflow.add_node("grade_documents", grade_documents)
workflow.add_node("generate", generate)
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query)
# 构建图的边
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
START,
route_question,
{
"web_search": "web_search",
"vectorstore": "retrieve",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("web_search", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "grade_documents")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"grade_documents",
decide_to_generate,
{
"transform_query": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "retrieve")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"generate",
grade_generation_v_documents_and_question,
{
"not supported": "generate",
"useful": END,
"not useful": "transform_query",
},
)
# 编译
app = workflow.compile()五、运行示例
示例 1:Web 搜索路由
python
inputs = {
"question": "What player at the Bears expected to draft first in the 2024 NFL draft?"
}
for output in app.stream(inputs):
for key, value in output.items():
pprint(f"Node '{key}':")
pprint("\n---\n")
pprint(value["generation"])执行流程:
---ROUTE QUESTION---
---ROUTE QUESTION TO WEB SEARCH---
---WEB SEARCH---
---GENERATE---
---CHECK HALLUCINATIONS---
---DECISION: GENERATION IS GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS---
---GRADE GENERATION vs QUESTION---
---DECISION: GENERATION ADDRESSES QUESTION---示例 2:向量存储路由
python
inputs = {"question": "What are the types of agent memory?"}
for output in app.stream(inputs):
for key, value in output.items():
pprint(f"Node '{key}':")
pprint("\n---\n")
pprint(value["generation"])执行流程:
---ROUTE QUESTION---
---ROUTE QUESTION TO RAG---
---RETRIEVE---
---CHECK DOCUMENT RELEVANCE TO QUESTION---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---
---DECISION: GENERATE---
---GENERATE---
---CHECK HALLUCINATIONS---
---DECISION: GENERATION IS GROUNDED IN DOCUMENTS---
---GRADE GENERATION vs QUESTION---
---DECISION: GENERATION ADDRESSES QUESTION---六、架构总结
Adaptive RAG 的核心流程:
用户查询
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 查询路由器 (Router) │
│ 分析查询 → 决定数据源 │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
├─→ Web 搜索 ────────────────────────────────────┐
│ │
└─→ 向量存储检索 │
│ │
▼ │
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐ │
│ 文档评分 (Grade Documents) │ │
│ 评估检索文档的相关性 │ │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘ │
│ │
├─→ 不相关 → 查询重写 → 重新检索 │
│ │
└─→ 相关 ─────────────────────────────────┤
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 生成答案 (Generate) │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 幻觉检测 (Hallucination) │
│ 答案是否基于检索内容? │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
├─→ 有幻觉 → 重新生成
│
▼
┌─────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 答案评估 (Answer Grader) │
│ 答案是否回答了问题? │
└─────────────────────────────────────┘
│
├─→ 未回答 → 查询重写
│
└─→ 已回答 → 返回结果七、关键设计要点
| 组件 | 作用 | 输出 |
|---|---|---|
| Query Router | 分析查询,路由到合适的数据源 | vectorstore / web_search |
| Retrieval Grader | 评估检索文档的相关性 | yes / no |
| Generator | 基于上下文生成答案 | 文本答案 |
| Hallucination Grader | 检测答案是否有幻觉 | yes / no |
| Answer Grader | 评估答案是否回答了问题 | yes / no |
| Question Rewriter | 优化查询以提高检索效果 | 优化后的查询 |
思考题
- 如何扩展路由器以支持更多数据源(如知识图谱、SQL 数据库)?
- 在什么情况下应该增加最大重试次数限制?
- 如何在生产环境中监控和调试 Adaptive RAG 工作流?