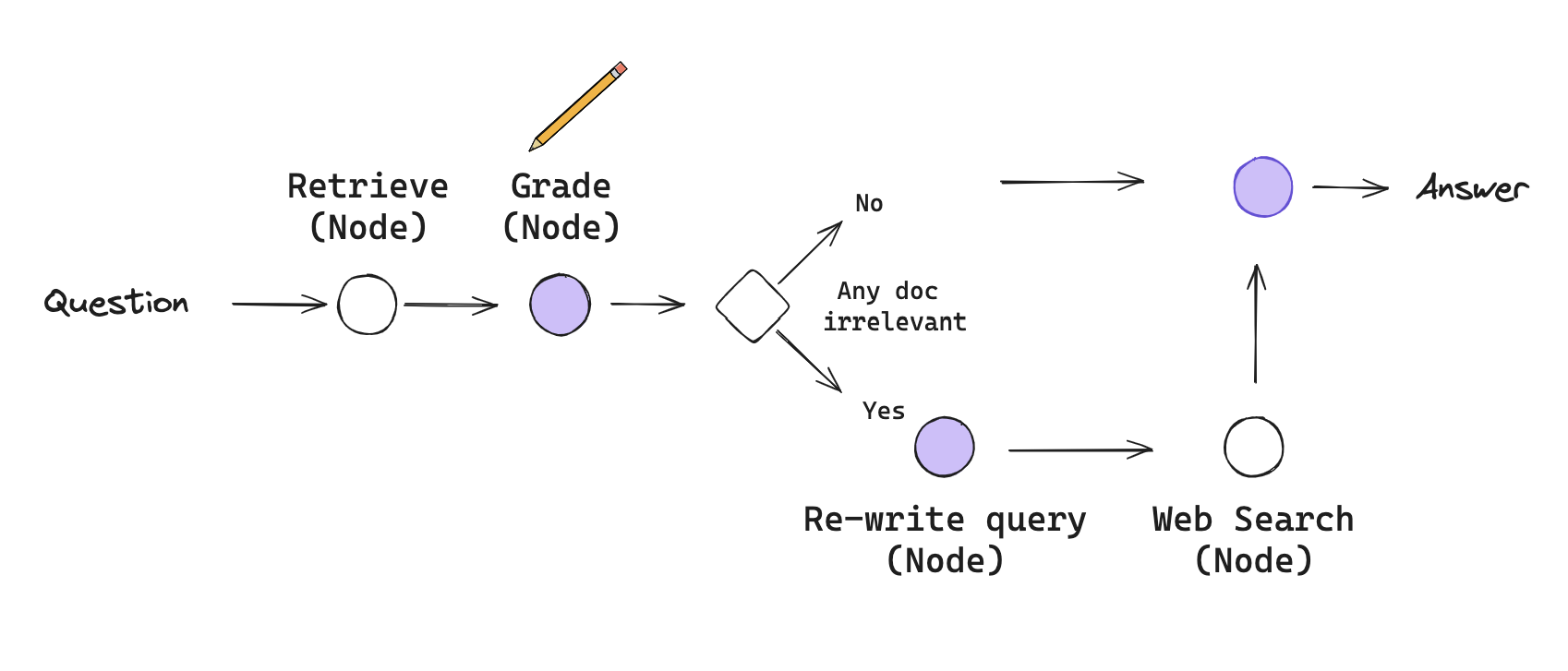
Corrective RAG (CRAG)
Corrective-RAG (CRAG) is a strategy for RAG that incorporates self-reflection / self-grading on retrieved documents.
In the paper here, a few steps are taken:
- If at least one document exceeds the threshold for relevance, then it proceeds to generation
- Before generation, it performs knowledge refinement
- This partitions the document into "knowledge strips"
- It grades each strip, and filters our irrelevant ones
- If all documents fall below the relevance threshold or if the grader is unsure, then the framework seeks an additional datasource
- It will use web search to supplement retrieval
We will implement some of these ideas from scratch using LangGraph:
- Let's skip the knowledge refinement phase as a first pass. This can be added back as a node, if desired.
- If any documents are irrelevant, let's opt to supplement retrieval with web search.
- We'll use Tavily Search for web search.
- Let's use query re-writing to optimize the query for web search.
Setup
First, let's download our required packages and set our API keys
pip install langchain_community tiktoken langchain-openai langchainhub chromadb langchain langgraph tavily-pythonimport getpass
import os
def _set_env(key: str):
if key not in os.environ:
os.environ[key] = getpass.getpass(f"{key}:")
_set_env("OPENAI_API_KEY")
_set_env("TAVILY_API_KEY")Tip: Set up LangSmith for LangGraph development
Sign up for LangSmith to quickly spot issues and improve the performance of your LangGraph projects. LangSmith lets you use trace data to debug, test, and monitor your LLM apps built with LangGraph - read more about how to get started here.
Create Index
Let's index 3 blog posts.
from langchain.text_splitter import RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter
from langchain_community.document_loaders import WebBaseLoader
from langchain_community.vectorstores import Chroma
from langchain_openai import OpenAIEmbeddings
urls = [
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-06-23-agent/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-03-15-prompt-engineering/",
"https://lilianweng.github.io/posts/2023-10-25-adv-attack-llm/",
]
docs = [WebBaseLoader(url).load() for url in urls]
docs_list = [item for sublist in docs for item in sublist]
text_splitter = RecursiveCharacterTextSplitter.from_tiktoken_encoder(
chunk_size=250, chunk_overlap=0
)
doc_splits = text_splitter.split_documents(docs_list)
# Add to vectorDB
vectorstore = Chroma.from_documents(
documents=doc_splits,
collection_name="rag-chroma",
embedding=OpenAIEmbeddings(),
)
retriever = vectorstore.as_retriever()LLMs
Note: Using Pydantic with LangChain
This notebook uses Pydantic v2
BaseModel, which requireslangchain-core >= 0.3. Usinglangchain-core < 0.3will result in errors due to mixing of Pydantic v1 and v2BaseModels.
Retrieval Grader
from langchain_core.prompts import ChatPromptTemplate
from langchain_openai import ChatOpenAI
from pydantic import BaseModel, Field
# Data model
class GradeDocuments(BaseModel):
"""Binary score for relevance check on retrieved documents."""
binary_score: str = Field(
description="Documents are relevant to the question, 'yes' or 'no'"
)
# LLM with function call
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-4o-mini", temperature=0)
structured_llm_grader = llm.with_structured_output(GradeDocuments)
# Prompt
system = """You are a grader assessing relevance of a retrieved document to a user question. \n
If the document contains keyword(s) or semantic meaning related to the question, grade it as relevant. \n
Give a binary score 'yes' or 'no' score to indicate whether the document is relevant to the question."""
grade_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system),
("human", "Retrieved document: \n\n {document} \n\n User question: {question}"),
]
)
retrieval_grader = grade_prompt | structured_llm_grader
question = "agent memory"
docs = retriever.invoke(question)
doc_txt = docs[1].page_content
print(retrieval_grader.invoke({"question": question, "document": doc_txt}))Generate
from langchain import hub
from langchain_core.output_parsers import StrOutputParser
# Prompt
prompt = hub.pull("rlm/rag-prompt")
# LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model_name="gpt-3.5-turbo", temperature=0)
# Post-processing
def format_docs(docs):
return "\n\n".join(doc.page_content for doc in docs)
# Chain
rag_chain = prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
# Run
generation = rag_chain.invoke({"context": docs, "question": question})
print(generation)Question Re-writer
# LLM
llm = ChatOpenAI(model="gpt-3.5-turbo-0125", temperature=0)
# Prompt
system = """You a question re-writer that converts an input question to a better version that is optimized \n
for web search. Look at the input and try to reason about the underlying semantic intent / meaning."""
re_write_prompt = ChatPromptTemplate.from_messages(
[
("system", system),
(
"human",
"Here is the initial question: \n\n {question} \n Formulate an improved question.",
),
]
)
question_rewriter = re_write_prompt | llm | StrOutputParser()
question_rewriter.invoke({"question": question})Web Search Tool
from langchain_community.tools.tavily_search import TavilySearchResults
web_search_tool = TavilySearchResults(k=3)Create Graph
Now let's create our graph that will use CRAG
Define Graph State
from typing import List
from typing_extensions import TypedDict
class GraphState(TypedDict):
"""
Represents the state of our graph.
Attributes:
question: question
generation: LLM generation
web_search: whether to add search
documents: list of documents
"""
question: str
generation: str
web_search: str
documents: List[str]Define Nodes
from langchain.schema import Document
def retrieve(state):
"""
Retrieve documents
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): New key added to state, documents, that contains retrieved documents
"""
print("---RETRIEVE---")
question = state["question"]
# Retrieval
documents = retriever.invoke(question)
return {"documents": documents, "question": question}
def generate(state):
"""
Generate answer
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): New key added to state, generation, that contains LLM generation
"""
print("---GENERATE---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
# RAG generation
generation = rag_chain.invoke({"context": documents, "question": question})
return {"documents": documents, "question": question, "generation": generation}
def grade_documents(state):
"""
Determines whether the retrieved documents are relevant to the question.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Updates documents key with only filtered relevant documents
"""
print("---CHECK DOCUMENT RELEVANCE TO QUESTION---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
# Score each doc
filtered_docs = []
web_search = "No"
for d in documents:
score = retrieval_grader.invoke(
{"question": question, "document": d.page_content}
)
grade = score.binary_score
if grade == "yes":
print("---GRADE: DOCUMENT RELEVANT---")
filtered_docs.append(d)
else:
print("---GRADE: DOCUMENT NOT RELEVANT---")
web_search = "Yes"
continue
return {"documents": filtered_docs, "question": question, "web_search": web_search}
def transform_query(state):
"""
Transform the query to produce a better question.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Updates question key with a re-phrased question
"""
print("---TRANSFORM QUERY---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
# Re-write question
better_question = question_rewriter.invoke({"question": question})
return {"documents": documents, "question": better_question}
def web_search(state):
"""
Web search based on the re-phrased question.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
state (dict): Updates documents key with appended web results
"""
print("---WEB SEARCH---")
question = state["question"]
documents = state["documents"]
# Web search
docs = web_search_tool.invoke({"query": question})
web_results = "\n".join([d["content"] for d in docs])
web_results = Document(page_content=web_results)
documents.append(web_results)
return {"documents": documents, "question": question}Define Edges
def decide_to_generate(state):
"""
Determines whether to generate an answer, or re-generate a question.
Args:
state (dict): The current graph state
Returns:
str: Binary decision for next node to call
"""
print("---ASSESS GRADED DOCUMENTS---")
state["question"]
web_search = state["web_search"]
state["documents"]
if web_search == "Yes":
# All documents have been filtered check_relevance
# We will re-generate a new query
print(
"---DECISION: ALL DOCUMENTS ARE NOT RELEVANT TO QUESTION, TRANSFORM QUERY---"
)
return "transform_query"
else:
# We have relevant documents, so generate answer
print("---DECISION: GENERATE---")
return "generate"Compile Graph
The just follows the flow we outlined in the figure above.
from langgraph.graph import END, StateGraph, START
workflow = StateGraph(GraphState)
# Define the nodes
workflow.add_node("retrieve", retrieve) # retrieve
workflow.add_node("grade_documents", grade_documents) # grade documents
workflow.add_node("generate", generate) # generate
workflow.add_node("transform_query", transform_query) # transform_query
workflow.add_node("web_search_node", web_search) # web search
# Build graph
workflow.add_edge(START, "retrieve")
workflow.add_edge("retrieve", "grade_documents")
workflow.add_conditional_edges(
"grade_documents",
decide_to_generate,
{
"transform_query": "transform_query",
"generate": "generate",
},
)
workflow.add_edge("transform_query", "web_search_node")
workflow.add_edge("web_search_node", "generate")
workflow.add_edge("generate", END)
# Compile
app = workflow.compile()Use the graph
from pprint import pprint
# Run
inputs = {"question": "What are the types of agent memory?"}
for output in app.stream(inputs):
for key, value in output.items():
# Node
pprint(f"Node '{key}':")
# Optional: print full state at each node
# pprint.pprint(value["keys"], indent=2, width=80, depth=None)
pprint("\n---\n")
# Final generation
pprint(value["generation"])from pprint import pprint
# Run
inputs = {"question": "How does the AlphaCodium paper work?"}
for output in app.stream(inputs):
for key, value in output.items():
# Node
pprint(f"Node '{key}':")
# Optional: print full state at each node
# pprint.pprint(value["keys"], indent=2, width=80, depth=None)
pprint("\n---\n")
# Final generation
pprint(value["generation"])